What are Quantum Computers?
Published on 30 Oct 2023
Other
Quantum computing is a relatively new, but promising technology. Several companies and groups are working in parallel on its development, and results are already quite promising. But, what are quantum computers, and what are their differences from are questions on which most of the people can not find answers, thus, we will explain this topic in this article.
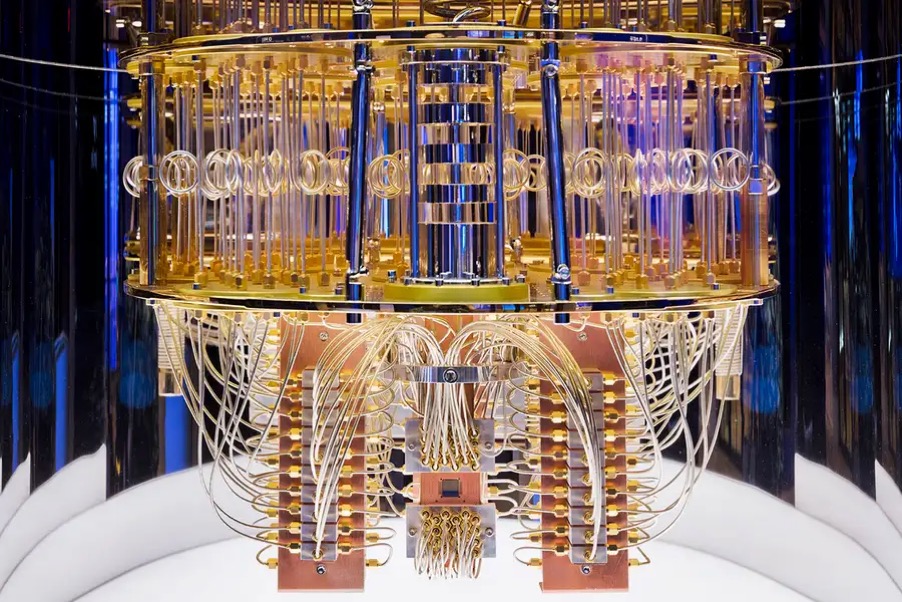
There is a myth that quantum computers are just powerful computing systems, because their structure is completely different. While classical computers are digital systems which work on bits which can have 2 possible values, either 1 or 0.They are built on transistor based technology which has existed since the 20th century. Number of CPU cores, RAM and any other parameters can be scaled to make a supercomputer, but the base, digital architecture, remains the same.
But there is a problem in conventional computers, even though they are fast, they struggle to solve complex problems, which involveы relationship and influence of many different parameters, for example creating atomic models. As Azure quantum documentation mentions, “Imagine a system of electrons where electrons can be in any 40 positions. The electrons then may be in any of 240 configurations .Storing in a conventional computer memory would require more than 130 GB of memory! If we allowed the particles to be in any of 41 positions, there would be twice as many configurations at 241 which in turn would require more than 260 GB of memory to store. At a few hundred electrons the memory required to store the system exceeds the number of particles in the universe; thus there is no hope with our conventional computers to ever simulate their quantum dynamics.”
For the aforementioned reasons, in the 1980s Richard Feynman proposed an idea to create a quantum computer and as we can see now, his idea has developed a lot since then, until in 2001 IBM made a 7 qubit processor, which found factors of 15.
Quantum Computers run on Qubits, it is true that it has 2 possible values, 0 and 1, however it can be in a linear combination of them, which is called a superposition, it means that they can represent both 0 and 1 at the same time. Usually, qubits are expressed as ψ=α∣0⟩+β∣1⟩ where α and β are complex numbers, absolute values of which represent the probability, or the weight, sum of which should always be equal to 1.
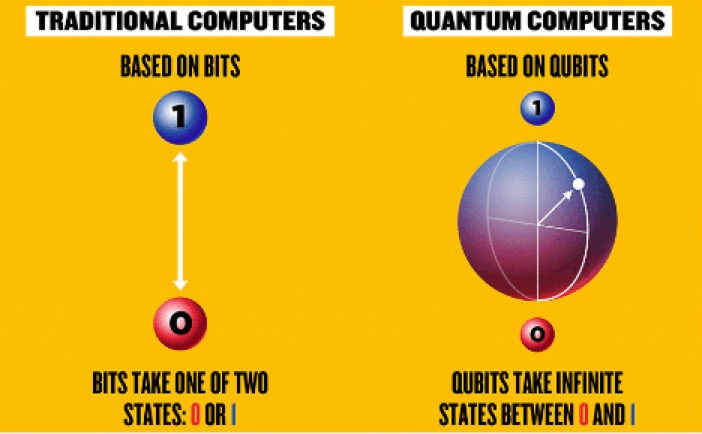
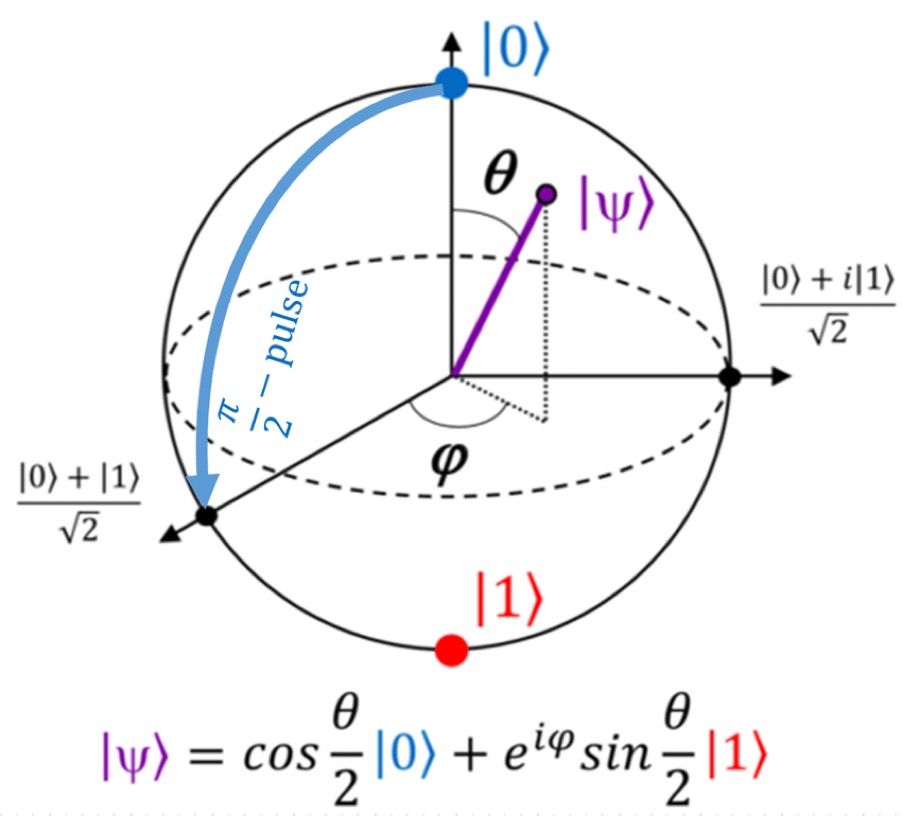
Since qubits consist of 2 complex numbers, we can not visualize it by the help of 2 dimensional models, because it consists of 4 parts-2 imaginary parts of alpha and beta and 2 real parts of alpha and beta. However, a swedish-american model, “Bloch’s Sphere” copes with this task. However, after finding the exponential form of the complex numbers and then simplifying them we can get a value with 3 “numbers” in it, which lets us illustrate it in a 3 dimensional model.
However, we are not developing quantum computers without a reason. There are a lot of uses possible for it. The first use is cryptography. Most encryptions could not be broken with conventional computers, while quantum computers are able to break them within minutes or even seconds. However, quantum computers can be a key to create new, better and more secure, forms of encryption.
Quantum computers can create immersive and realistic gaming, as well as development of new genres and platforms. They can create complex graphics, physics, sound effects, adaptive scenarios and even hyper-realistic non-playable-characters.
Artificial intelligence can also be enchanted by the help of quantum computers. As it was mentioned before, conventional computer systems struggle with massive amounts of parallel data which have relationships between each other. This could be fixed by the help of quantum computing to process that humongous data and to enchant deep learning.
Discoveries of drugs, vaccines and new medicine can be done with the help of quantum computers, as well as discovery of new materials, such as superconductors, superfluids etc. Quantum computers can make extremely complex calculations required for the design of aforementioned things.
Maybe the closest possible application of it is weather prediction. Ray Johnson, the ex CTO at Lockheed Martin and now an director at quantum startup Rigetti Computing believe that quantum computing’s method of simultaneous calculation will likely be successful in “analyzing the very, very complex system of variables that is weather.”
We also should mention that quantum computers can also be a sufficient instrument for optimizing many large problems in logistics, finance, manufacturing and engineering. They can have unmeasurable benefits in database management and research processes.
In conclusion, considering everything mentioned before we might be sure that quantum computing is the future of computing machines, and their potential and possible future contribution to science is unmeasurable.